UET Vision
UET Mission
To generate knowledge for global competitive advantage and become a leading world class research University
To play a leading role as a University of Engineering and Technology in teaching, research, innovation, and commercialization that is internationally relevant and has a direct bearing on national industrial, technological, and socio-economic development
Civil Engineering Program Mission
To impart high quality civil engineering education through modern teaching and research for the national and international socio-economic development
Program Educational Objectives (PEOs)
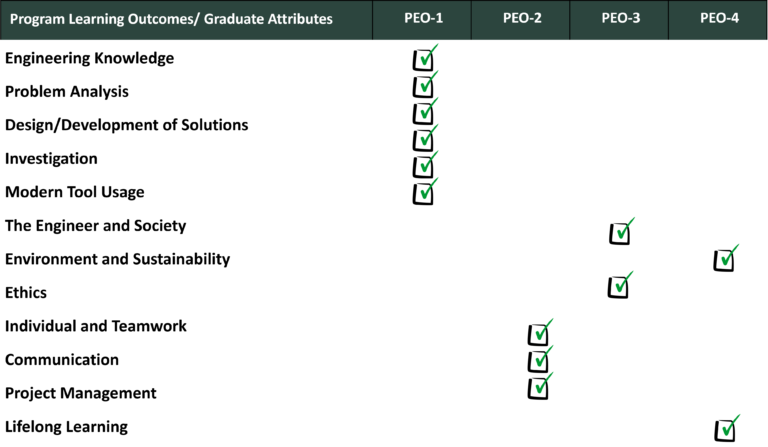
- Graduates demonstrate their proficiency of applying the knowledge & skills to solve complex civil engineering problems.
- Graduates communicate effectively and contribute in the project team.
- Graduates uphold principles of ethics and societal obligations with integrity throughout their professional practices.
- Graduates engage themselves in continuous professional learning process for the sustainability.

Program Learning Outcomes (PLOS)
Program Learning Outcomes (PLOs) are traits that the program wants to inculcate in its graduates by the time of graduation. It is expected that by the time of graduation the students must have attained a specific set of knowledge, skills, and behavioral traits. PLOs can be accessed through the UET website via the following link:
Following PLOs have been selected for the B.Sc. Civil Engineering Program.
- Engineering Knowledge: An ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, engineering fundamentals, and an engineering specialization to the solution of complex engineering problems.
- Problem Analysis: An ability to identify, formulate, research literature, and analyze complex engineering problems reaching substantiated conclusions using first principles of mathematics, natural sciences and engineering sciences.
- Design/Development of Solutions: An ability to design solutions for complex engineering problems and design systems, components or processes that meet specified needs with appropriate consideration for public health and safety, cultural, societal, and environmental considerations.
- Investigation: An ability to investigate complex engineering problems in a methodical way including literature survey, design and conduct of experiments, analysis and interpretation of experimental data, and synthesis of the information to derive valid conclusions.
- Modern Tool Usage: An ability to create, select and apply appropriate techniques, resources, and modern engineering and IT tools, including prediction and modeling, to complex engineering activities, with an understanding of the limitations.
- The Engineer and Society: An ability to apply to reason informed by the contextual knowledge to assess societal, health, safety, legal and cultural issues and the consequent responsibilities relevant to professional engineering practice and solution to complex engineering problems.
- Environment and Sustainability: An ability to understand the impact of professional engineering solutions in societal and environmental contexts and demonstrate knowledge of and need for sustainable development.
- Ethics: Apply ethical principles and commit to professional ethics and responsibilities and norms of engineering practice.
- Individual and Team Work: An ability to work effectively, as an individual or in a team, on multifaceted and /or multidisciplinary settings.
- Communication: An ability to communicate effectively, orally as well as in writing, on complex engineering activities with the engineering community and with society at large, such as being able to comprehend and write effective reports and design documentation, make effective presentations, and give and receive clear instructions.
- Project Management: An ability to demonstrate management skills and apply engineering principles to one’s own work, as a member and/or leader in a team, to manage projects in a multidisciplinary environment.
- Life-long Learning: An ability to recognize importance of, and pursuing life-long learning in the broader context of innovation and technological developments.
MAPPING OF PEOS TO PLOS